
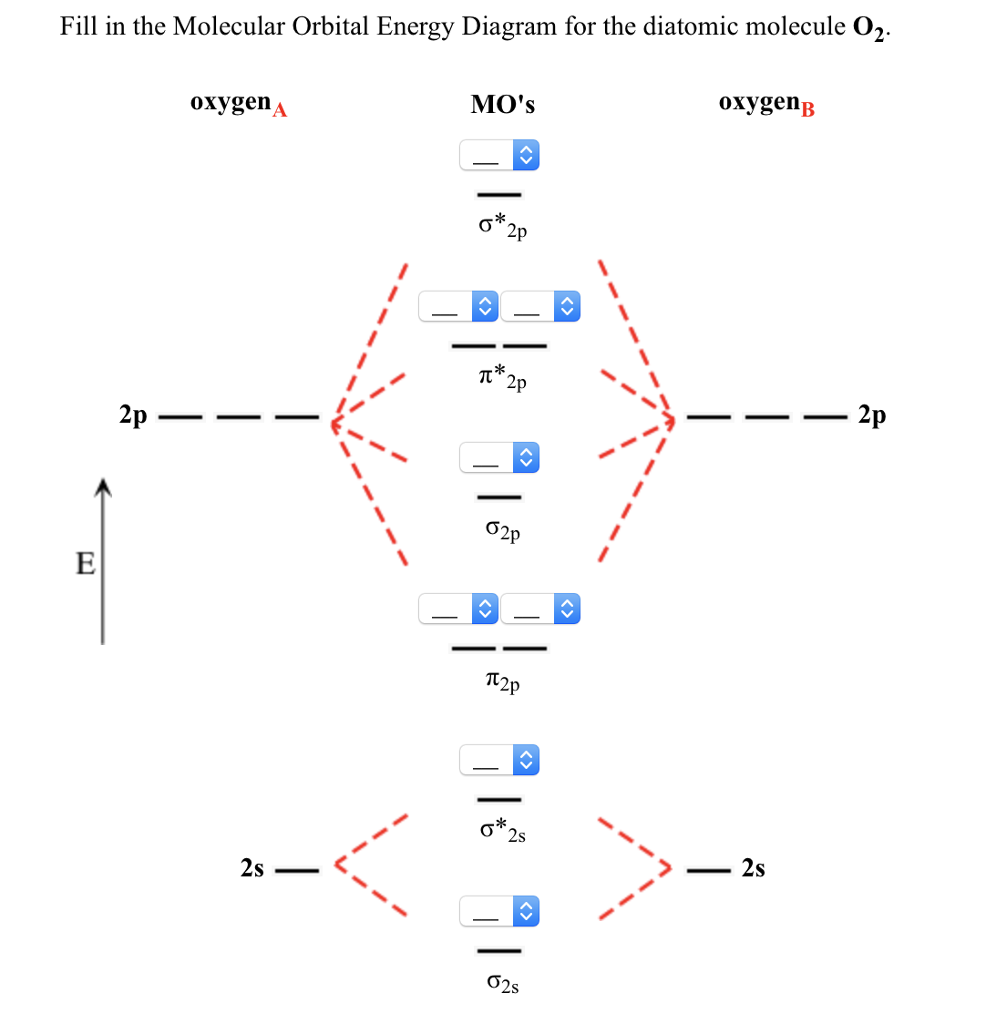
The mathematical process of combining atomic orbitals to generate molecular orbitals is called the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO). In these diatomic molecules, several types of molecular orbitals occur. Such molecules are called homonuclear diatomic molecules.
Before we turn our attention to the MO diagram of dioxygen. We will consider the molecular orbitals in molecules composed of two identical atoms (H 2 or Cl 2, for example). A fundamental rule of molecular orbital theory is that the number of molecular orbitals must.
#No molecular orbital diagram full
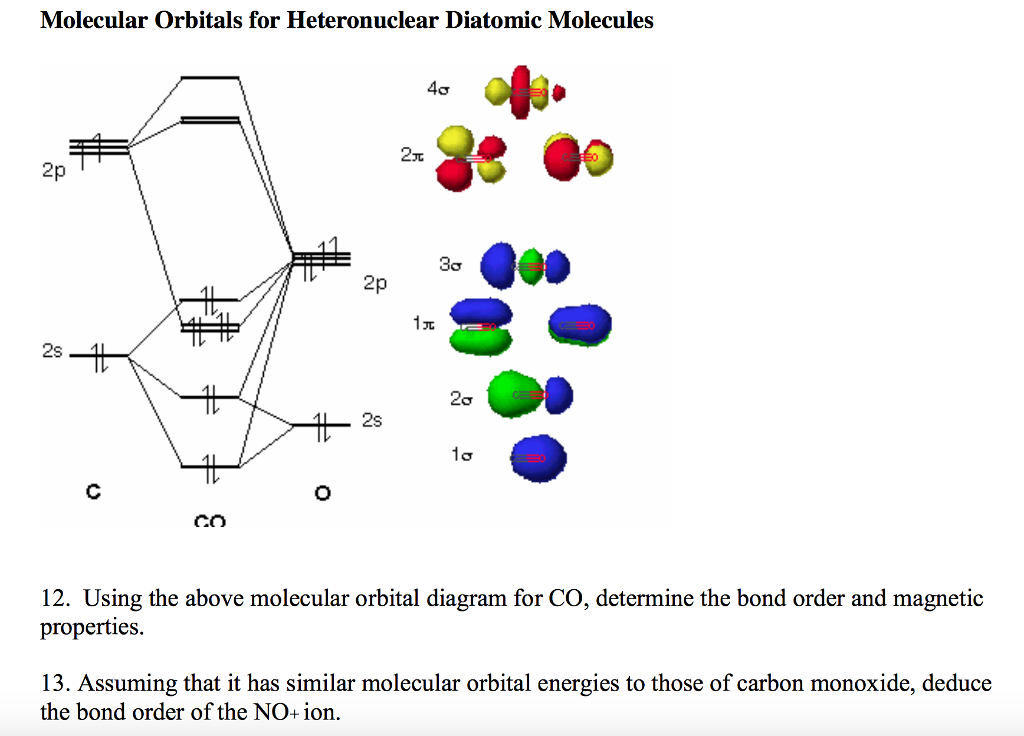
Like an atomic orbital, a molecular orbital is full when it contains two electrons with opposite spin. (1s)2( 1s)2(2s)2( 2s)2(2px)2(2py)2(2pz)2( 2px)1 This requires that we know what the molecular orbital (MO) diagram is for NO here it is ( Miessler et al., Answer Key ): (The original was this I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels.
#No molecular orbital diagram for free
The region of space in which a valence electron in a molecule is likely to be found is called a molecular orbital ( Ψ 2). For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of electr. Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in molecules are limited to discrete (quantized) energies. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Needs multiple structures to describe resonance Predicts the arrangement of electrons in molecules Predicts molecular shape based on the number of regions of electron density lie at higher energy than the s2p, draw MO energy diagrams and predict the bond order in a molecule or ion with each number of total valence electrons. Nitrogen atom has 2p atomic orbitals lower by 2.52 eV, and 2s atomic orbitals lower by 6.13 eV than with carbon atom. Thus, simply add one or two electrons into the 2b3u and 2b2u to get NO2 and NO 2, respectively. \) : Comparison of Bonding Theories Valence Bond TheoryĬonsiders bonds as localized between one pair of atomsĬonsiders electrons delocalized throughout the entire moleculeĬreates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d…) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp 2, sp 3…)Ĭombines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*)Ĭreates bonding and antibonding interactions based on which orbitals are filled You've seen the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of CO2: CO2 and NO+ 2 are isoelectronic and thus have the same electron configuration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
